Institute Output

General Relativistic Hydrodynamics in Discrete Spacetime: Perfect Fluid Accretion onto Static and Spinning Black Holes
Jonathan Gorard
This study investigates the effect of spacetime discretization on accretion dynamics of a relativistic fluid onto a spinning black hole, specifically noting that accretion rates decrease with increased discretization scale and that drag force sensitivity and instabilities intensify at critical discretization values.

Computational General Relativity in the Wolfram Language using Gravitas II: ADM Formalism and Numerical Relativity
Jonathan Gorard
This paper introduces the Gravitas computational general relativity framework's numerical subsystem, emphasizing its ability to perform 3 + 1 spacetime decompositions via the ADM formalism, handle complex simulations of gravitational phenomena like binary black hole mergers, and leverage adaptive refinement algorithms based on hypergraph rewriting within the Wolfram Language.
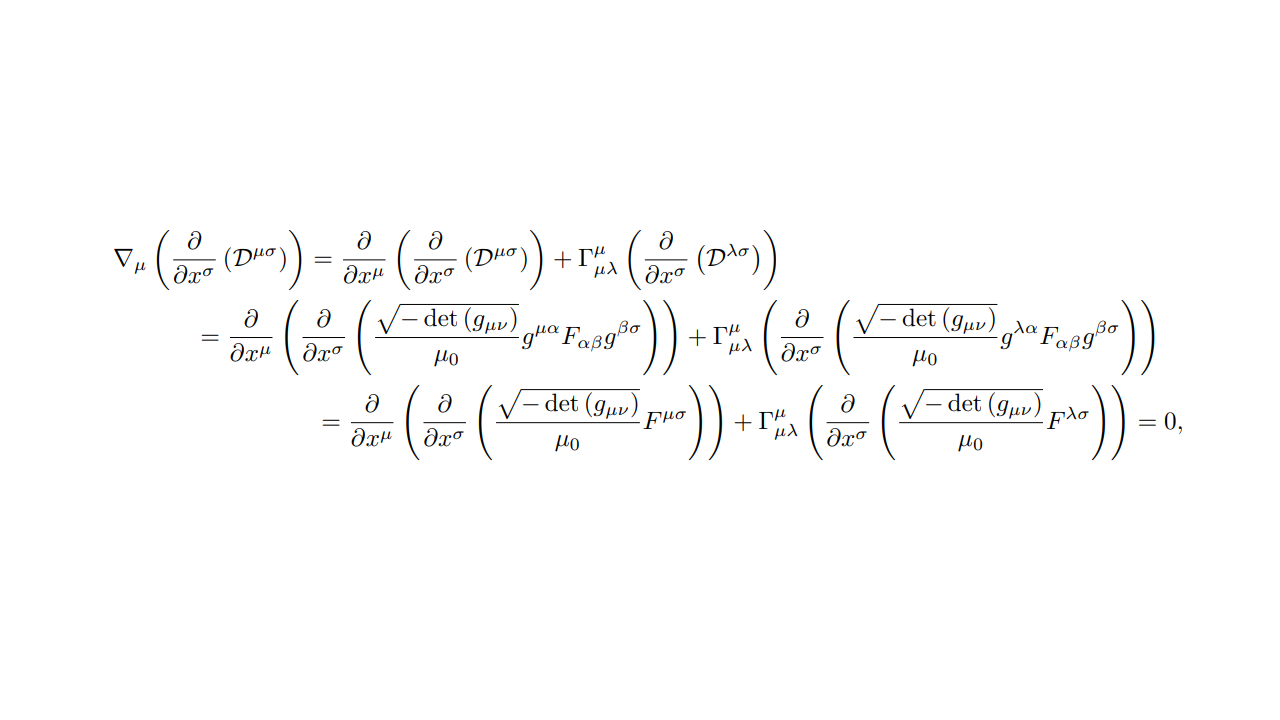
Computational General Relativity in the Wolfram Language using Gravitas I: Symbolic and Analytic Computation
Jonathan Gorard
Gravitas introduces a robust computational framework for general relativity in the Wolfram Language, featuring seamless integration of symbolic and numerical tools to handle complex spacetime geometries and solve the Einstein field equations.

Non-Vacuum Solutions, Gravitational Collapse and Discrete Singularity Theorems in Wolfram Model Systems
Jonathan Gorard
This study extends the Raychaudhuri equation to discrete spacetimes, exploring conditions under which they might exhibit geodesic incompleteness, and applies numerical simulations to predict black hole formations.
Axiomatic Quantum Field Theory in Discrete Spacetime via Multiway Causal Structure: The Case of Entanglement Entropies
Jonathan Gorard, Julia Dannemann-Freitag
This research examines a covariant approach to entanglement entropy in discrete quantum gravity, comparing causal set and Wolfram model frameworks to reveal a monotonic relationship.

A Cosine Rule-Based Discrete Sectional Curvature for Graphs
Xerxes D. Arsiwalla, J.F. Du Plessis
How does one generalize differential geometric constructs such as curvature of a manifold to the discrete world of graphs and other combinatorial structures? This problem carries significant importance for analyzing models of discrete spacetime in quantum gravity; inferring network geometry in network science; and manifold learning in data science. The key contribution of this paper is to introduce and validate a new estimator of discrete sectional curvature for random graphs with low metric-distortion.

A Functorial Perspective on (Multi)computational Irreducibility
Jonathan Gorard
This article aims to provide a novel formalization of the concept of computational irreducibility in terms of the exactness of functorial correspondence between a category of data structures and elementary computations and a corresponding category of (1-dimensional) cobordisms.
Homotopies in Multiway (Non-Deterministic) Rewriting Systems as n-Fold Categories
Xerxes D. Arsiwalla, Jonathan Gorard, Hatem Elshatlawy
Pregeometric Spaces from Wolfram Model Rewriting Systems as Homotopy Types
Xerxes D. Arsiwalla, Jonathan Gorard
The study explores how spatial structures in physics can emerge from pregeometric combinatorial models governed by computational rules, using higher category theory and homotopy types.

Some Relativistic and Gravitational Properties of the Wolfram Model
Jonathan Gorard
The article shows that causal invariance in the Wolfram Model leads to discrete general and Lorentz covariance, introducing curvature concepts for hypergraphs related to the Ricci tensor and Einstein field equations

Algorithmic Causal Sets and the Wolfram Model
Jonathan Gorard
This study links causal set theory and the Wolfram model, showing hypergraph rewriting facilitates causal set evolution, infers conformal invariance, and derives the Benincasa-Dowker action from discrete Einstein-Hilbert action.

Hypergraph Discretization of the Cauchy Problem in General Relativity via Wolfram Model Evolution
Jonathan Gorard
This article introduces a numerical general relativity code using the Z4 formulation with hypergraph-based Cauchy data and adaptive mesh refinement, validating results against standard spacetimes and comparing with Wolfram model evolution.
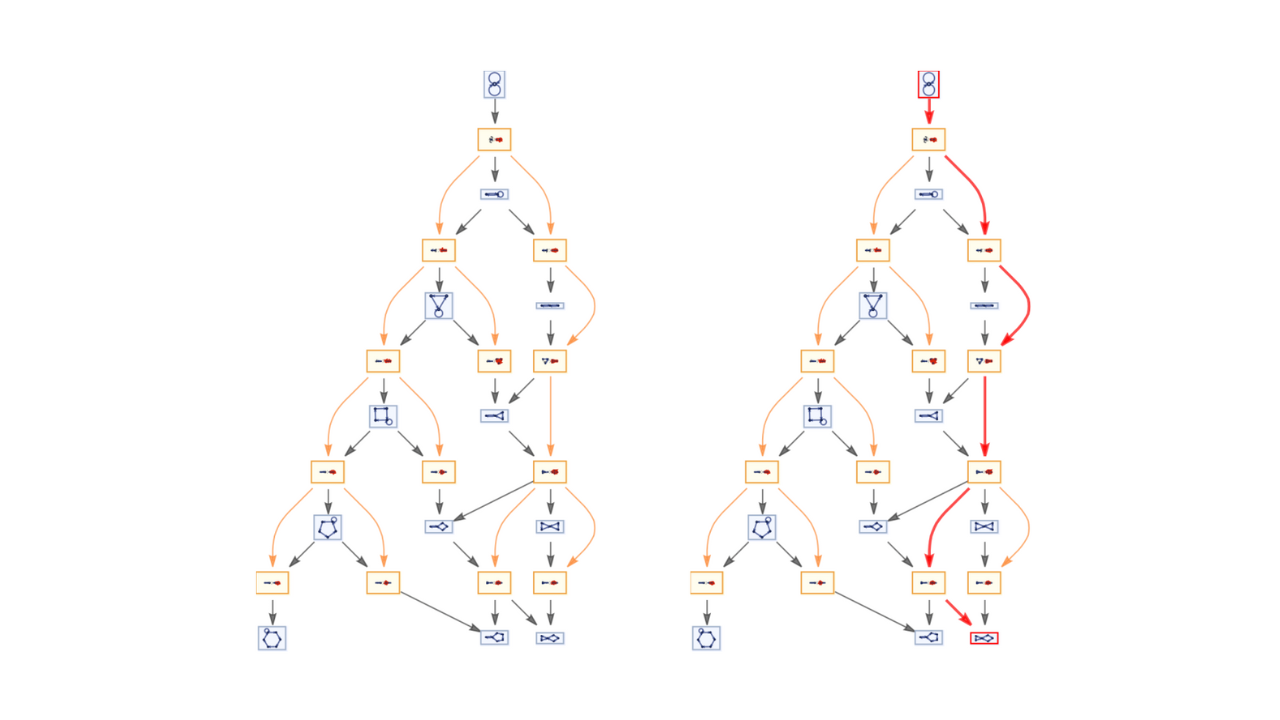
Fast Automated Reasoning over String Diagrams using Multiway Causal Structure
Jonathan Gorard, Manojna Namuduri, Xerxes D. Arsiwalla

ZX-Calculus and Extended Wolfram Model Systems II: Fast Diagrammatic Reasoning with an Application to Quantum Circuit Simplification
Jonathan Gorard, Manojna Namuduri, Xerxes D. Arsiwalla
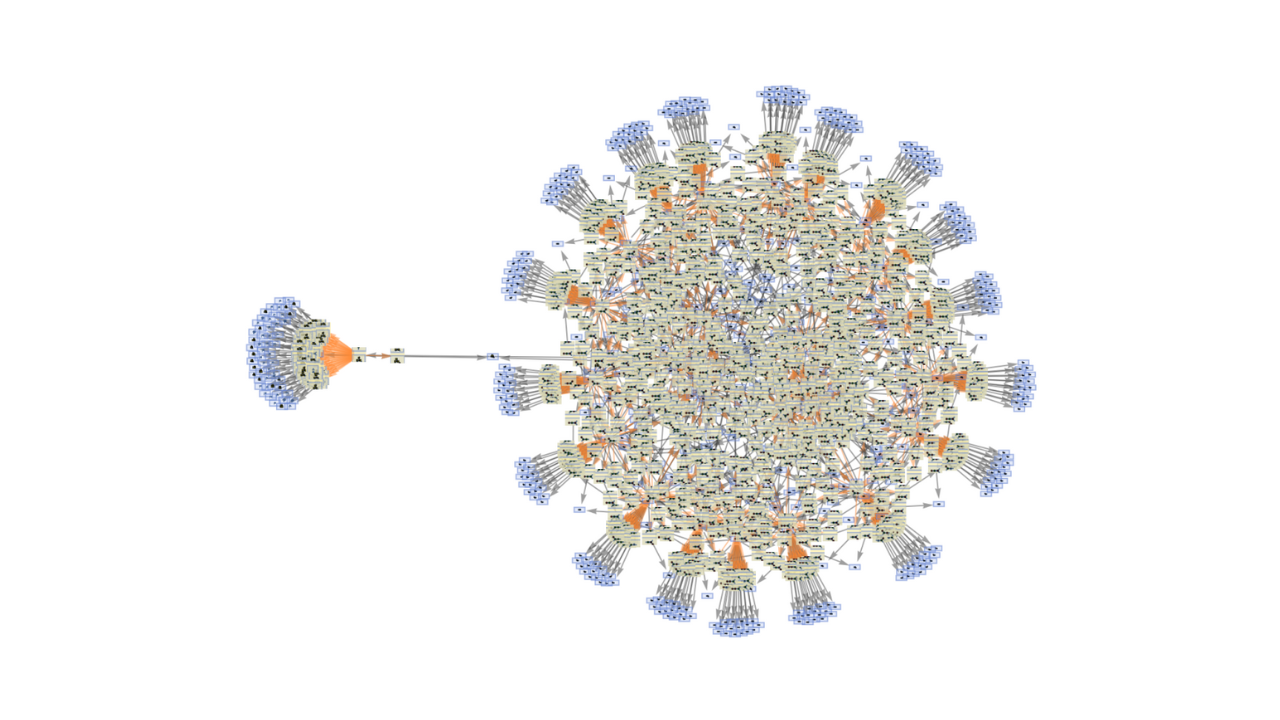
ZX-Calculus and Extended Hypergraph Rewriting Systems I: A Multiway Approach to Categorical Quantum Information Theory
Jonathan Gorard, Manojna Namuduri, Xerxes D. Arsiwalla

Some Quantum Mechanical Properties of theWolfram Model
Jonathan Gorard
By exploring hypergraph rules that deliberately break causal invariance, we show that the Wolfram Model’s multiway evolution functions like a quantum superposition whose geometry converges to projective Hilbert space. By proving that observers can “collapse” these histories via Knuth–Bendix completion—and deriving multiway analogues of Einstein’s equations, the path integral and the Schrödinger equation—we unify discrete spacetime, quantum mechanics and relativity within one framework.
