Institute Output
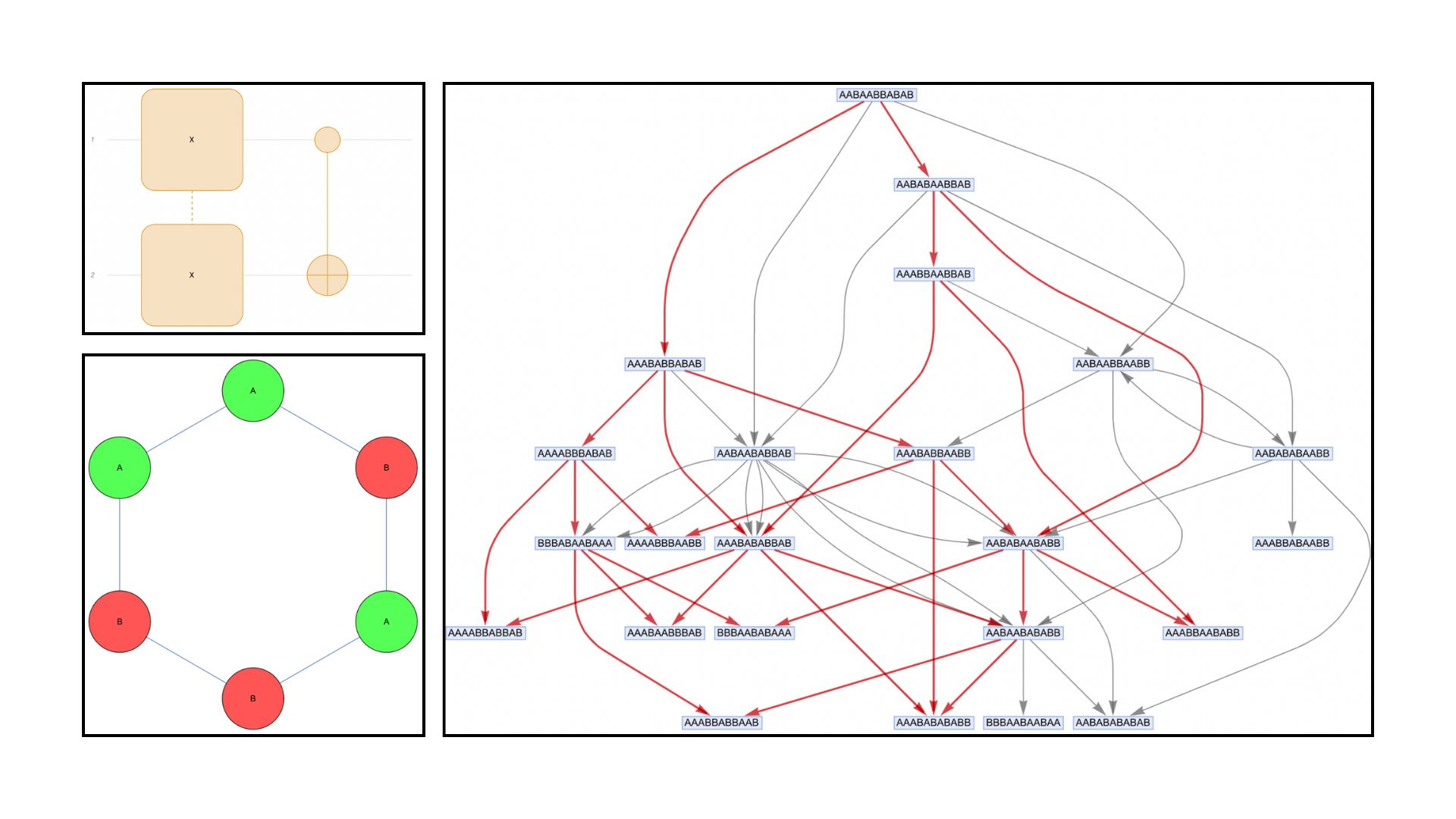
Quantum Operators From Wolfram Model Multiway Systems
Furkan Semih Dündar, Xerxes D. Arsiwalla, Hatem Elshatlawy
Using Wolfram Model multiway rewriting systems we have found that by using multiway systems one can construct representations of quantum circuits, showing that one can encode the Hadamard gate, the π/8 gate and the CNOT using multiway rewriting systems. This suggests the possibility of universal quantum computation using multiway rewriting.
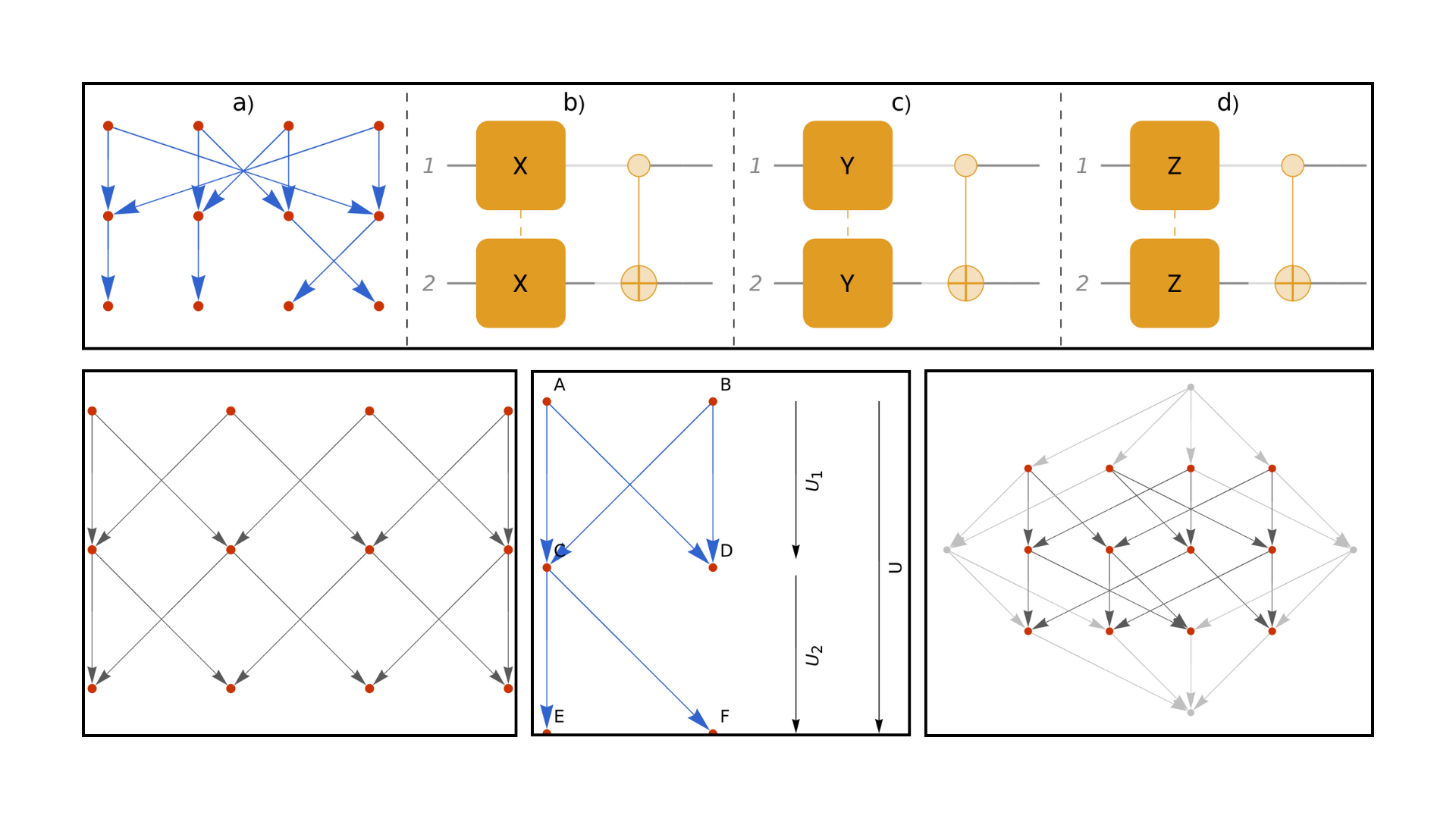
Quantum Gates from Wolfram Model Multiway Rewriting Systems
Furkan Semih Dündar, Xerxes D. Arsiwalla, Hatem Elshatlawy
We show how representations of finite-dimensional quantum operators can be constructed using nondeterministic rewriting systems. In particular, we investigate Wolfram model multiway rewriting systems based on string substitutions.

What’s Special about Life? Bulk Orchestration and the Rulial Ensemble in Biology and Beyond
Stephen Wolfram
It’s a key feature of living systems, perhaps even in some ways the key feature: that even right down to a molecular scale, things are orchestrated. Molecules (or at least large ones) don’t just move around randomly, like in a liquid or a gel. Instead, what molecular biology has discovered is that there are endless active mechanisms that in effect orchestrate what even individual molecules in living systems do. But what is the result of all that orchestration? And could there perhaps be a general characterization of what happens in systems that exhibit such “bulk orchestration”?

The Ruliology of Lambdas
Stephen Wolfram
It’s a story of pure, abstract computation. In fact, historically, one of the very first. But even though it’s something I for one have used in practice for nearly half a century, it’s not something that in all my years of exploring simple computational systems and ruliology I’ve ever specifically studied. And, yes, it involves some fiddly technical details. But it’ll turn out that lambdas—like so many systems I’ve explored—have a rich ruliology, made particularly significant by their connection to practical computing.

On the Nature of Time
Stephen Wolfram
Time is a central feature of human experience. But what actually is it? In traditional scientific accounts it’s often represented as some kind of coordinate much like space (though a coordinate that for some reason is always systematically increasing for us). But while this may be a useful mathematical description, it’s not telling us anything about what time in a sense “intrinsically is”.

Observer Theory
Stephen Wolfram
We call it perception. We call it measurement. We call it analysis. But in the end it’s about how we take the world as it is, and derive from it the impression of it that we have in our minds.

Aggregation and Tiling as Multicomputational Processes
Stephen Wolfram
Multiway systems have a central role in our Physics Project, particularly in connection with quantum mechanics. But what’s now emerging is that multiway systems in fact serve as a quite general foundation for a whole new “multicomputational” paradigm for modeling.

Expression Evaluation and Fundamental Physics
Stephen Wolfram
It is shown that way the Wolfram Language rewrites and evaluates expressions mirrors the universe’s own evolution: both proceed through discrete events linked by causal relationships, form “spacetime-like” structures and branch into multiway histories analogous to quantum superpositions.
Axiomatic Quantum Field Theory in Discrete Spacetime via Multiway Causal Structure: The Case of Entanglement Entropies
Jonathan Gorard, Julia Dannemann-Freitag
This research examines a covariant approach to entanglement entropy in discrete quantum gravity, comparing causal set and Wolfram model frameworks to reveal a monotonic relationship.

Games and Puzzles as Multicomputational Systems
Stephen Wolfram
Multicomputation is one of the core ideas of the Wolfram Physics Project—and in particular is at the heart of our emerging understanding of quantum mechanics. But how can one get an intuition for what is initially the rather abstract idea of multicomputation? A good approach, I believe, is to see it in action in familiar systems and situations. And I explore here what seems like a particularly good example: games and puzzles.

On the Concept of Motion
Stephen Wolfram
It seems like the kind of question that might have been hotly debated by ancient philosophers, but would have been settled long ago: how is it that things can move? And indeed with the view of physical space that’s been almost universally adopted for the past two thousand years it’s basically a non-question. As crystallized by the likes of Euclid it’s been assumed that space is ultimately just a kind of “geometrical background” into which any physical thing can be put—and then moved around.

Multicomputation with Numbers: The Case of Simple Multiway Systems
Stephen Wolfram
Multicomputation is an important new paradigm, but one that can be quite difficult to understand. Here my goal is to discuss a minimal example: multiway systems based on numbers. Many general multicomputational phenomena will show up here in simple forms (though others will not). And the involvement of numbers will often allow us to make immediate use of traditional mathematical methods.

Multicomputation: A Fourth Paradigm for Theoretical Science
Stephen Wolfram
One might have thought it was already exciting enough for our Physics Project to be showing a path to a fundamental theory of physics and a fundamental description of how our physical universe works. But what I’ve increasingly been realizing is that actually it’s showing us something even bigger and deeper: a whole fundamentally new paradigm for making models and in general for doing theoretical science. And I fully expect that this new paradigm will give us ways to address a remarkable range of longstanding central problems in all sorts of areas of science—as well as suggesting whole new areas and new directions to pursue.

The Problem of Distributed Consensus
Stephen Wolfram
In any decentralized system with computers, people, databases, measuring devices or anything else one can end up with different values or results at different “nodes”. But for all sorts of reasons one often wants to agree on a single “consensus” value, that one can for example use to “make a decision and go on to the next step”.
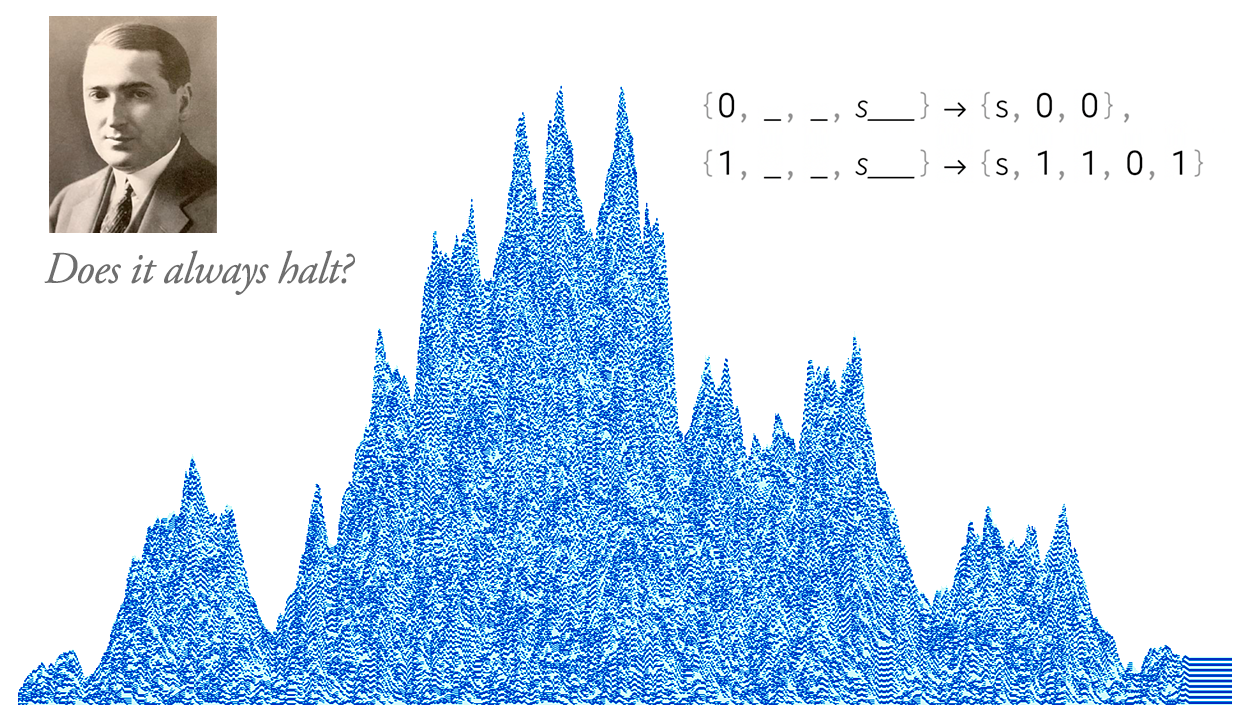
After 100 Years, Can We Finally Crack Post’s Problem of Tag? A Story of Computational Irreducibility, and More
Stephen Wolfram
For Post, the failure to crack his system derailed his whole intellectual worldview. For me now, the failure to crack Post’s system in a sense just bolsters my worldview—providing yet more indication of the strength and ubiquity of computational irreducibility and the Principle of Computational Equivalence.

Multiway Turing Machines
Stephen Wolfram
Over the years I’ve studied the simplest ordinary Turing machines quite a bit, but I’ve barely looked at multiway Turing machines (also known as nondeterministic Turing machines or NDTMs). Recently, though, I realized that multiway Turing machines can be thought of as “maximally minimal” models both of concurrent computing and of the way we think about quantum mechanics in our Physics Project. So now this piece is my attempt to “do the obvious explorations” of multiway Turing machines.

Faster than Light in Our Model of Physics: Some Preliminary Thoughts
Stephen Wolfram
“So you think you have a fundamental theory of physics. Well, then tell us if warp drive is possible!” Despite the hopes and assumptions of science fiction, real physics has for at least a century almost universally assumed that no genuine effect can ever propagate through physical space any faster than light. But is this actually true? We’re now in a position to analyze this in the context of our model for fundamental physics. And I’ll say at the outset that it’s a subtle and complicated question, and I don’t know the full answer yet.

Event Horizons, Singularities and Other Exotic Spacetime Phenomena
Stephen Wolfram
In our models, space emerges as the large-scale limit of our spatial hypergraph, while spacetime effectively emerges as the large-scale limit of the causal graph that represents causal relationships between updating events in the spatial hypergraph. An important result is that (subject to various assumptions) there is a continuum limit in which the emergent spacetime follows Einstein’s equations from general relativity.

Finally We May Have a Path to the Fundamental Theory of Physics… and It’s Beautiful
Stephen Wolfram
It’s unexpected, surprising—and for me incredibly exciting. To be fair, at some level I’ve been working towards this for nearly 50 years. But it’s just in the last few months that it’s finally come together. And it’s much more wonderful, and beautiful, than I’d ever imagined.
